EGZERSİZ VE ALZHEIMER
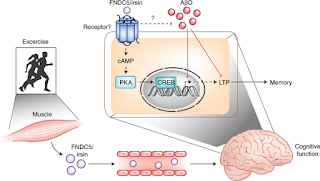 Nature Medicine’de yayımlanan bir araştırma, egzersizin insanlarda hafıza ve düşünmeyi nasıl koruduğu konusunda yol gösterebilir.
Nature Medicine’de yayımlanan bir araştırma, egzersizin insanlarda hafıza ve düşünmeyi nasıl koruduğu konusunda yol gösterebilir.
Daha önce yapılan araştırmalar egzersizin beyin sağlığını nasıl koruduğunu ve düşünmeyi etkilediğini göstermişti. Egzersiz aynı zamanda nöronlar arasındaki sinaptik iletiyi ve sinapsların işlevini de geliştirebilir.
Alzheimer ve demasnla ilgili egzersizin bu hastalıkların ilerlemesini yavaşlatabileceği ve yine bu hastalıklara yakalanma riskini azaltacağı gösterilmişti.Alzheimer ve demasnla ilgili egzersizin bu hastalıkların ilerlemesini yavaşlatabileceği ve yine bu hastalıklara yakalanma riskini azaltacağı gösterilmişti.
Bu gelişmeler bir yana 2012 yılında tespit edilen ve ismini mitolojiden alan İrisin hormonu, egzersiz sırasında kaslardan salınıyor ve metabolizmayı hızlandırıp ısı açığa çıkarıyor. İrisin; lipit dokuda UCP1 salınmasını sağlayan ve böylece termogenez ve kilo kaybı ile sonuçlanan reaksiyonlara sebep olan anahtar hormon olup, vücut kitle endeksinin düzenlenmesinde görevli.
Alzheimer hastalığında da beyin hücreklerinin enerjiyi kullanma şeklindeki değişikliklere inanıldığı için beyinde İrisin seviyelerini artırarak beyin sağlığının korunacağını düşündü.
Önce İrisin’in beyinde var olduğunu gösteren araştırmacılar, demanslı farelerin beynine konsantre irisin enjeksiyonu yaptı. Bu farelerin kısa bir süre sonra hafıza testlerinde daha iyi performans gösterdikleri ve sinaptik iletideki gelişmeleri gözlemledi.
Araştırmacılar son olarak 5 hafta boyunca günde bir saat yüzme egzersizi yaptıkları farelerde İrisinle ilgili aynı etkiyi gözlemledi.
İRİSİN
 İrisin beyaz yağ dokusunu kahverengi yağ dokusuna çevirerek enerji harcanmasını sağlayan termojenik bir proteindir. 2012 yılında Boström ve
ark., sistematik egzersiz yapıldığında, kişiyi metabolik hastalıklardan ruyan ve egzersiz sonrası iskelet kasından salınan
bir protein keşfetmişlerdir. Bu bir membran proteini olup fibronektin tip III domain 5 (FNDC5) olarak adlandırılmış ve bu proteinin dolaşıma proteoliz
sonrası salındığı anlaşılmıştır. FNDC5 ayrıca, fibronektin tip III tekrarlarını içeren protein 2 (FRCP2)
ve Pep olarak da adlandırılmaktadır. FNDC5 proteininin proteolitik ürününe irisin adı verilmiştir.
İskelet kasından salınan irisin otokrin, parakrin ve
endokrin etkili bir hormondur. İrisin hormonunun
adı mitolojik kahraman olan İris’ten gelmektedir.
İrisin beyaz yağ dokusunu kahverengi yağ dokusuna çevirerek enerji harcanmasını sağlayan termojenik bir proteindir. 2012 yılında Boström ve
ark., sistematik egzersiz yapıldığında, kişiyi metabolik hastalıklardan ruyan ve egzersiz sonrası iskelet kasından salınan
bir protein keşfetmişlerdir. Bu bir membran proteini olup fibronektin tip III domain 5 (FNDC5) olarak adlandırılmış ve bu proteinin dolaşıma proteoliz
sonrası salındığı anlaşılmıştır. FNDC5 ayrıca, fibronektin tip III tekrarlarını içeren protein 2 (FRCP2)
ve Pep olarak da adlandırılmaktadır. FNDC5 proteininin proteolitik ürününe irisin adı verilmiştir.
İskelet kasından salınan irisin otokrin, parakrin ve
endokrin etkili bir hormondur. İrisin hormonunun
adı mitolojik kahraman olan İris’ten gelmektedir.
İrisin; Boström ve ark. tarafından ilk kez kas dokudan izole edilmiş, 12 kDa ağırlığında ve 112 amino
asitten oluşan glukoprotein yapılı bir hormondur. İrisin; FNDC5 molekülünün proteolitik bir ürünüdür. Bu reseptör uygun membrana bağlanmayı sağlayan, daha sonra bölünecek olan bir N-terminal
sinyal sekansı içermektedir. Bu sinyal sekansını Nterminal FNIII benzeri alan ve esnek C-terminal
kuyruk içeren irisin domainini takip eder. İrisin domaini, kısa bir transmembranel bölge ile sitozolik
bölgeye bağlıdır. İrisin domaininin matür FNDC5’in
proteolitik bir ürünü olduğu varsayılmaktadır. İrisin hormonunun yapısının insan ve farelerde %100
benzer olduğu bildirilmiştir. İrisin sentezleyen başlıca dokular Tablo 1’de görülmektedir.
İRİSİNİN EGZERSİZLE İLİŞKİSİ
 Boström ve ark., insanlarda ve farelerde egzersiz
sonrasında iskelet kasında FNDC5 mRNA’sının artmış olduğunu rapor etmişlerdir. FNDC5 ekspresyonu sırasında fare karaciğerinde oluşan
değişiklikleri araştırmak için, vektör olarak adenovirüsler seçilmiş ve karaciğere enjekte edilmiştir.
Bu işlemden sonra farelerin kahverengi yağ dokusunda uzun yapılı FNDC5’in aşırı salgılandığı tespit
edilmiştir. Hofmann ve ark., egzersiz ve irisin arasındaki bağlantıyı açıklamaya çalışmışlardır. Anoreksiya nervozalı erişkinler üzerinde yaptıkları
çalışma sonucunda, egzersizle irisin düzeyleri arasında korelasyon olmadığını belirlemişlerdir. Timmons ve ark., 24 erişkin genç erkekte altı haftalık egzersiz programından sonra yapılan iskelet
kası biyopsilerinde, FNDC5’in mRNA miktarının değişmediğini bildirmişlerdir. Aynı araştırma grubunun yaptığı bir başka çalışmada, 20-80 yaş arası
43 erişkinde, 20 haftalık kontrollü ve sıkı antrenman sonucu yapılmış biyopsilerde bir değişiklik
gözlenmemiştir. Aynı çalışmada 10 yaşlı, 10 genç
bireyde zorlayıcı bir egzersiz programı uyguladıktan sonra yapılan biyopsilerde, yaşlı bireylerde
FNDC5 mRNA’sında %30’luk bir artış gözlemlemişlerdir. Timmons ve ark. yapmış oldukları çalışmaların sonucuna göre, egzersiz sonrasında irisin
düzeyinde artış olup olmadığı hakkında genelleme
yapmanın doğru olmadığını rapor etmişlerdir. Castillo-Quan’ın yaptığı bir çalışmada, farelerde egzersiz sonrası irisin düzeylerinin %65 oranında arttığı gözlenmiştir. Lecker ve ark., sistolik kalp
yetmezliği olan 24 hastada düşük ve yüksek aerobik
performans sonrası FNDC5’in mRNA’sını ölçmüşler ve yüksek aerobik performans sonrası FNDC5
mRNA’sında artış kaydetmişler, ancak plazma irisin düzeyini ölçmemişlerdir. Aerobik egzersiz,
kasta oksijen tüketimini yükseltmekte ve oksijen
pik seviyesini artırmaktadır. FNDC5 ve PGC1α
düzeylerinin oksijen hacmi (VO2) düzeyinin pik
yaptığı grupta en yüksek seviyede olduğu gözlenmiştir. Başka bir çalışmada, diyabetik olmayan erkeklerin oluşturduğu bir gruba 10 hafta boyunca
aerobik egzersiz yaptırılmış ve egzersiz öncesi ve
sonrası kan ve kas biyopsi örnekleri alınmıştır. Egzersiz sonrası dolaşımdaki irisin düzeyinin iki katına çıktığı bildirilmiştir. Bununla beraber, ailesel
olarak hiperkolesterolemik ve normal olan domuzlarda deltoid ve triceps brachii’deki FNDC5 mRNA
düzeylerinin karşılaştırılması sonucu, mRNA düzeylerinde bir fark olmadığı gözlenmemiş, ancak
irisin sirkülasyonunun hiperkolesterolemik olan
grupta arttığı görülmüştür. Hecksteden ve ark., 26
hafta boyunca haftada üç kez yapılan egzersizin irisin sirkülasyonunda herhangi bir değişiklik yapmadığını bildirmişlerdir. Raschke ve ark., egzersiz
öncesi ve sonrasında farelerden alınan iskelet kası
biyopsilerinde FNDC5 mRNA’sında herhangi bir
değişiklik gözlemlememişlerdir. Scharhag-Rosenberg ve ark., 37’si kontrol grubu olmak üzere 74
kişi ile yaptıkları altı aylık bir çalışma sonucunda
serbest yağ kütlesi ile metabolik hız ya da irisin
hormonu arasında bir korelasyon olmadığını belirtmişlerdir. Ayrıca in vitro olarak insan primer
kas hücreleri ile de çalışmalar yapılmıştır. Bu çalışmalardan birinde, egzersizi taklit eden forskolin ve
ionomisin tedavisi uygulanmış ve PGC1α
mRNA’sının kasta iki katına çıktığı, FNDC5
mRNA’sının %18 oranında, irisinin ise ortalama
%20 arttığı belirtilmiştir. Sonuç olarak, insan iskelet kaslarında irisinin düzenlenmesi konusunda
hâlâ soru işaretleri olduğu bildirilmiştir.
Boström ve ark., insanlarda ve farelerde egzersiz
sonrasında iskelet kasında FNDC5 mRNA’sının artmış olduğunu rapor etmişlerdir. FNDC5 ekspresyonu sırasında fare karaciğerinde oluşan
değişiklikleri araştırmak için, vektör olarak adenovirüsler seçilmiş ve karaciğere enjekte edilmiştir.
Bu işlemden sonra farelerin kahverengi yağ dokusunda uzun yapılı FNDC5’in aşırı salgılandığı tespit
edilmiştir. Hofmann ve ark., egzersiz ve irisin arasındaki bağlantıyı açıklamaya çalışmışlardır. Anoreksiya nervozalı erişkinler üzerinde yaptıkları
çalışma sonucunda, egzersizle irisin düzeyleri arasında korelasyon olmadığını belirlemişlerdir. Timmons ve ark., 24 erişkin genç erkekte altı haftalık egzersiz programından sonra yapılan iskelet
kası biyopsilerinde, FNDC5’in mRNA miktarının değişmediğini bildirmişlerdir. Aynı araştırma grubunun yaptığı bir başka çalışmada, 20-80 yaş arası
43 erişkinde, 20 haftalık kontrollü ve sıkı antrenman sonucu yapılmış biyopsilerde bir değişiklik
gözlenmemiştir. Aynı çalışmada 10 yaşlı, 10 genç
bireyde zorlayıcı bir egzersiz programı uyguladıktan sonra yapılan biyopsilerde, yaşlı bireylerde
FNDC5 mRNA’sında %30’luk bir artış gözlemlemişlerdir. Timmons ve ark. yapmış oldukları çalışmaların sonucuna göre, egzersiz sonrasında irisin
düzeyinde artış olup olmadığı hakkında genelleme
yapmanın doğru olmadığını rapor etmişlerdir. Castillo-Quan’ın yaptığı bir çalışmada, farelerde egzersiz sonrası irisin düzeylerinin %65 oranında arttığı gözlenmiştir. Lecker ve ark., sistolik kalp
yetmezliği olan 24 hastada düşük ve yüksek aerobik
performans sonrası FNDC5’in mRNA’sını ölçmüşler ve yüksek aerobik performans sonrası FNDC5
mRNA’sında artış kaydetmişler, ancak plazma irisin düzeyini ölçmemişlerdir. Aerobik egzersiz,
kasta oksijen tüketimini yükseltmekte ve oksijen
pik seviyesini artırmaktadır. FNDC5 ve PGC1α
düzeylerinin oksijen hacmi (VO2) düzeyinin pik
yaptığı grupta en yüksek seviyede olduğu gözlenmiştir. Başka bir çalışmada, diyabetik olmayan erkeklerin oluşturduğu bir gruba 10 hafta boyunca
aerobik egzersiz yaptırılmış ve egzersiz öncesi ve
sonrası kan ve kas biyopsi örnekleri alınmıştır. Egzersiz sonrası dolaşımdaki irisin düzeyinin iki katına çıktığı bildirilmiştir. Bununla beraber, ailesel
olarak hiperkolesterolemik ve normal olan domuzlarda deltoid ve triceps brachii’deki FNDC5 mRNA
düzeylerinin karşılaştırılması sonucu, mRNA düzeylerinde bir fark olmadığı gözlenmemiş, ancak
irisin sirkülasyonunun hiperkolesterolemik olan
grupta arttığı görülmüştür. Hecksteden ve ark., 26
hafta boyunca haftada üç kez yapılan egzersizin irisin sirkülasyonunda herhangi bir değişiklik yapmadığını bildirmişlerdir. Raschke ve ark., egzersiz
öncesi ve sonrasında farelerden alınan iskelet kası
biyopsilerinde FNDC5 mRNA’sında herhangi bir
değişiklik gözlemlememişlerdir. Scharhag-Rosenberg ve ark., 37’si kontrol grubu olmak üzere 74
kişi ile yaptıkları altı aylık bir çalışma sonucunda
serbest yağ kütlesi ile metabolik hız ya da irisin
hormonu arasında bir korelasyon olmadığını belirtmişlerdir. Ayrıca in vitro olarak insan primer
kas hücreleri ile de çalışmalar yapılmıştır. Bu çalışmalardan birinde, egzersizi taklit eden forskolin ve
ionomisin tedavisi uygulanmış ve PGC1α
mRNA’sının kasta iki katına çıktığı, FNDC5
mRNA’sının %18 oranında, irisinin ise ortalama
%20 arttığı belirtilmiştir. Sonuç olarak, insan iskelet kaslarında irisinin düzenlenmesi konusunda
hâlâ soru işaretleri olduğu bildirilmiştir.
KAYNAKLAR
1. Boström P, Wu J, Jedrychowski MP, Korde A, Ye L, Lo JC, et al. A PGC1-α dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat andthermogenesis. Nature 2012;481(7382):463- 8.
2. Ferrer-Martínez A, Ruiz-Lozano P, Chien KR. Mouse PeP: a novel peroxisomal protein linked to myoblast differentiation and development. Dev Dyn 2002;224(2):154-67.
3. Teufel A, Malik N, Mukhopadhyay M, Westphal H. FRCP1 and FRCP2, two novel fibronectin type III repeat containing genes. Gene 2002;297(1-2):79- 83.
4. Irving BA, Still CD, Argyropoulos G. Does IRISIN have a brite future as a therapeutic agent in humans? Curr Obes Rep 2014;3:235-41.
5. Grimal P. The Dictionary of Classical Mythology. 1st ed. Oxford. Wiley-Blackwell; 1996. p.614.
6. Schumacher MA, Chinnam N, Ohashi T, Shah RS, Erickson HP. The structure of irisin reveals a novel intersubunit β-sheet fibronectin type III (FNIII) dimer: implications for receptor activation. J Biol Chem 2013;288(47):33738-44.
7. Aydin S. Three new players in energy regulation: preptin, adropin and irisin. Peptides 2014;56:94- 110.
8. Brenmoehl J, Albrecht E, Komolka K, Schering L, LanghammerM, Hoeflich A, et al. Irisin is elevated in skeletalmuscle and serumofmice immediately after acute exercise. Int J Biol Sci 2014;10(3):338-49.
9. Xiong XQ, Chen D, Sun HJ, Ding L, Wang JJ, Chen Q, et al. FNDC5 overexpression and irisin ameliorate glucose/lipid metabolic derangements and enhance lipolysis in obesity. Biochim Biophys Acta 2015;1852(9):1867-75.
10. Erickson HP. Irisin and FNDC5 in retrospect: an exercise hormone or a trans-membrane receptor? Adipocyte 2013;2(4)289-93.
11. Hofmann T, Elbelt U, Ahnis A, Kobelt P, Rose M, Stengel A. Irisin levels are not affected by physical activity in patients with anorexia nervosa. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2014;4:202.
12. Timmons JA, Baar K, Davidsen PK, Atherton PJ. Is irisin a human exercise gene. Nature 2012;488(7413):E9-10.
13. Castillo-Quan JI. From white to brown fat through the PGC1-α dependent myokine irisin: implications for diabetes and obesity. Dis Model Mec 2012;5(3):293-5.
14. Lecker SH, Zavin A, Cao P, Arena R, Allsup K, Daniels KM, et al. Expression of the irisin precursor FNDC5 in skeletal muscle correlates with aerobic exercise performance in patients with heart failure. Circ Heart Fail 2012;5(6): 812-8.
15. Lian W, Gu X, Qin Y, Zheng X. Elevated plasma levels of adropin in heart failure patients. Int Med 2011;50(15):1523-7.
16. Mandic S, Myers J, Selig SE, Levinger I. Resistance versus aerobic exercisetraining in chronic heart failure. Curr Heart Fail Rep 2012;9(1):57-64.
17. Besse-Patin A, Montastier E, Vinel C, CastanLaurell I, Louche K, Dray C, et al. Effect of endurance training on skeletal muscle myokine expression in obesemen: identification of apelin as a novel myokine. Int J Obes (Lond) 2014;38(5): 707-13.
18. Fain JN, JM Şirketi, Booth FW, Laughlin MH, Padilla J, Jenkins NT ve diğerleri. Egzersiz eğitimi domuzlarda FNDC5 proteini veya mRNA ekspresyonunu arttırmaz. Metabolizma 2013; 62 (10): 1503-11.
19. Hecksteden A, Wegmann M, Steffen A, Kraushaar J, Morsch A, Ruppenthal S, vd. İrisin ve insanlarda egzersiz eğitimi-randomize kontrollü bir eğitim çalışmasının sonuçları. BMC Med 2013; 11: 235.
20. Raschke S, Elsen M, Gassenhuber H, Sommerfeld M, Schwahn U, Brockmann B, vd. İrisinin insanlarda yararlı bir etkisine karşı kanıt. Plos One 2013; 8 (9): e73680.
1. Boström P, Wu J, Jedrychowski MP, Korde A, Ye L, Lo JC, et al. A PGC1-α dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat andthermogenesis. Nature 2012;481(7382):463- 8.
2. Ferrer-Martínez A, Ruiz-Lozano P, Chien KR. Mouse PeP: a novel peroxisomal protein linked to myoblast differentiation and development. Dev Dyn 2002;224(2):154-67.
3. Teufel A, Malik N, Mukhopadhyay M, Westphal H. FRCP1 and FRCP2, two novel fibronectin type III repeat containing genes. Gene 2002;297(1-2):79- 83.
4. Irving BA, Still CD, Argyropoulos G. Does IRISIN have a brite future as a therapeutic agent in humans? Curr Obes Rep 2014;3:235-41.
5. Grimal P. The Dictionary of Classical Mythology. 1st ed. Oxford. Wiley-Blackwell; 1996. p.614.
6. Schumacher MA, Chinnam N, Ohashi T, Shah RS, Erickson HP. The structure of irisin reveals a novel intersubunit β-sheet fibronectin type III (FNIII) dimer: implications for receptor activation. J Biol Chem 2013;288(47):33738-44.
7. Aydin S. Three new players in energy regulation: preptin, adropin and irisin. Peptides 2014;56:94- 110.
8. Brenmoehl J, Albrecht E, Komolka K, Schering L, LanghammerM, Hoeflich A, et al. Irisin is elevated in skeletalmuscle and serumofmice immediately after acute exercise. Int J Biol Sci 2014;10(3):338-49.
9. Xiong XQ, Chen D, Sun HJ, Ding L, Wang JJ, Chen Q, et al. FNDC5 overexpression and irisin ameliorate glucose/lipid metabolic derangements and enhance lipolysis in obesity. Biochim Biophys Acta 2015;1852(9):1867-75.
10. Erickson HP. Irisin and FNDC5 in retrospect: an exercise hormone or a trans-membrane receptor? Adipocyte 2013;2(4)289-93.
11. Hofmann T, Elbelt U, Ahnis A, Kobelt P, Rose M, Stengel A. Irisin levels are not affected by physical activity in patients with anorexia nervosa. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2014;4:202.
12. Timmons JA, Baar K, Davidsen PK, Atherton PJ. Is irisin a human exercise gene. Nature 2012;488(7413):E9-10.
13. Castillo-Quan JI. From white to brown fat through the PGC1-α dependent myokine irisin: implications for diabetes and obesity. Dis Model Mec 2012;5(3):293-5.
14. Lecker SH, Zavin A, Cao P, Arena R, Allsup K, Daniels KM, et al. Expression of the irisin precursor FNDC5 in skeletal muscle correlates with aerobic exercise performance in patients with heart failure. Circ Heart Fail 2012;5(6): 812-8.
15. Lian W, Gu X, Qin Y, Zheng X. Elevated plasma levels of adropin in heart failure patients. Int Med 2011;50(15):1523-7.
16. Mandic S, Myers J, Selig SE, Levinger I. Resistance versus aerobic exercisetraining in chronic heart failure. Curr Heart Fail Rep 2012;9(1):57-64.
17. Besse-Patin A, Montastier E, Vinel C, CastanLaurell I, Louche K, Dray C, et al. Effect of endurance training on skeletal muscle myokine expression in obesemen: identification of apelin as a novel myokine. Int J Obes (Lond) 2014;38(5): 707-13.
18. Fain JN, JM Şirketi, Booth FW, Laughlin MH, Padilla J, Jenkins NT ve diğerleri. Egzersiz eğitimi domuzlarda FNDC5 proteini veya mRNA ekspresyonunu arttırmaz. Metabolizma 2013; 62 (10): 1503-11.
19. Hecksteden A, Wegmann M, Steffen A, Kraushaar J, Morsch A, Ruppenthal S, vd. İrisin ve insanlarda egzersiz eğitimi-randomize kontrollü bir eğitim çalışmasının sonuçları. BMC Med 2013; 11: 235.
20. Raschke S, Elsen M, Gassenhuber H, Sommerfeld M, Schwahn U, Brockmann B, vd. İrisinin insanlarda yararlı bir etkisine karşı kanıt. Plos One 2013; 8 (9): e73680.



